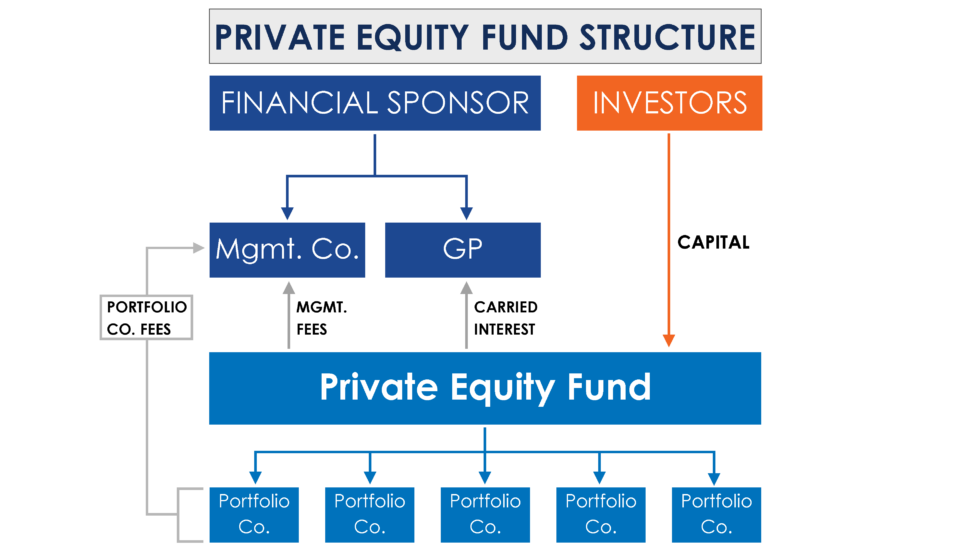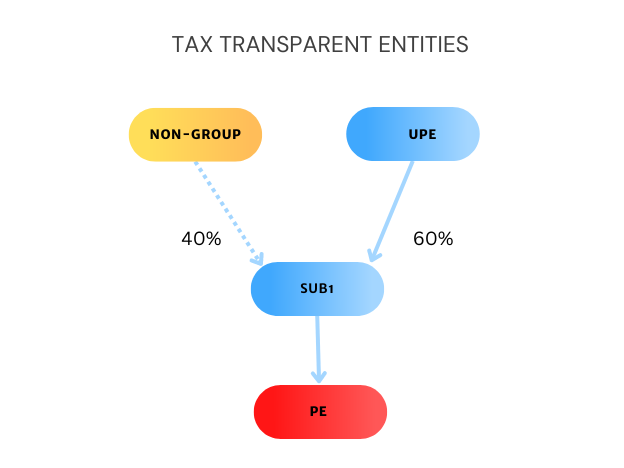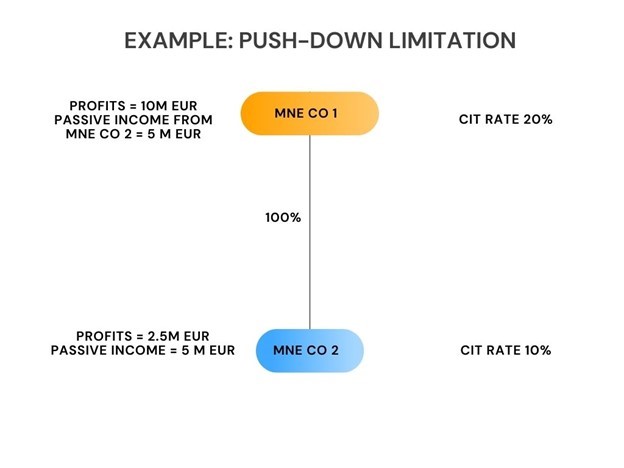
Differences Between Domestic CFC Regimes and the GloBE Rules That Allow Cross-Jurisdictional Blending
The definition of CFC taxes that are restricted in the GloBE rules is much narrower than under many domestic CFC regimes. In this article we look at this issue.