
Australia Issues a Draft Law to Amend Global Minimum Tax Rules
On February 16, 2026, Australia issued the Taxation (Multinational—Global and Domestic Minimum Tax)
Amendment (2026 Measures No.1) Rules 2026, to amend its Global Minimum Tax Rules.
Article 10 of the OECD Model Rules defines an entity as either:
– a legal person (except an individual); or
– any arrangement that prepares separate financial accounts.
Note that the First Set of OECD Administrative Guidance also excludes government agencies (both central and local government) that carry out government functions.
The first limb above would generally catch foundations, whilst the second would catch trusts.
This means that trusts and foundations are squarely within the Pillar Two rules and could be a low-taxed entity, an intermediate entity/partially owned parent entity or even an ultimate parent entity (UPE).
Under Article 1.4.1 of the OECD Model Rules, a UPE for the Pillar Two rules is:
Whether a trust is a UPE is an important consideration as (1) in many cases the UPE is required to apply the income inclusion rule to account for top-up tax and (2) the definition of an MNE group hinges on the relationship between the group companies and the UPE.
For instance, take this scenario:
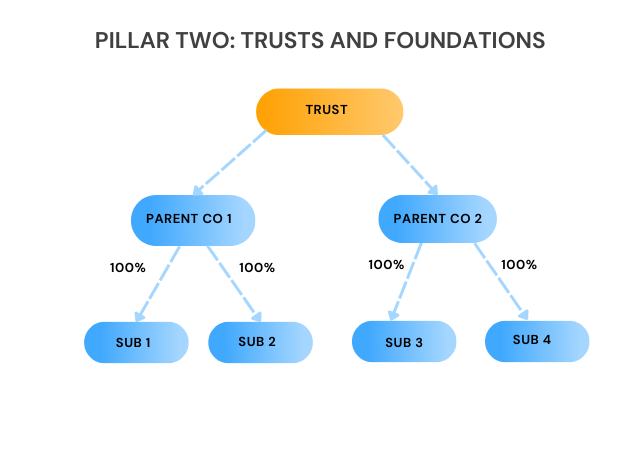
Determining if the trust was the UPE could result in all companies then potentially being within the scope of the Pillar Two rules (subject to any specific exclusions etc). Aside from the application of Pillar Two to the group, the trust could then be liable to account for top-up tax.
This in itself could create issues.
The definition of a group in the Pillar Two rules relies on accounting principles so that there is a group if there is a requirement to prepare consolidated financial statements.
Whilst a trust or foundation may not usually have to prepare consolidated financial statements under an accounting standard, the Pillar Two rules go further.
Article 10 of the OECD Model Rules states that if no consolidated financial statements are prepared a deeming provision applies so that the entity must prepare hypothetical consolidated financial statements as if it was required to prepare them in accordance with an Authorised Financial Accounting Standard that is either an Acceptable Financial Accounting Standard or another financial accounting standard.
As such, a trust or foundation would need to determine if it would be required to prepare accounting standards under an accounting standard.
This would again depend on accounting principles.
Under IFRS for instance, there is a requirement to consolidate if the trust or foundation possesses power over the parent entities, has exposure to variable returns from its involvement with them and has the ability to use its power over them to affect its returns.

On February 16, 2026, Australia issued the Taxation (Multinational—Global and Domestic Minimum Tax)
Amendment (2026 Measures No.1) Rules 2026, to amend its Global Minimum Tax Rules.

On February 13, 2026, Poland issued a draft law to amend its Global Minimum Tax Law for the December 2023, June 2024 and January 2025 OECD Administrative Guidance. This also includes QDMTT changes, including the introduction of a Local Financial Accounting Standard rule.

On February 12, 2026, Cabinet Resolution No. (2) of 2026, was published in the Official Gazette to provide for the detailed implementation of the IIR and QDMTT in Qatar.

On February 6, 2026, the Italian Revenue Agency approved the model for the GloBE tax Return. This is a consolidated form with information on the calculation of top-up tax under the IIR, UTPR and QDMTT.

On January 29, 2026, Canada’s Department of Finance released draft GMTA technical amendments introducing an elective private investment entity de-consolidation rule for Pillar Two/GMTA purposes.

On January 30, 2026, Japan’s National Tax Agency issued a law implementation circular clarifying certain aspects of its UTPR and QDMTT.

In January 2026, Canada issued the filing procedures for the GIR, GMT Return and the Double Filing Relief Notification.

On January 19, 2026, South Korea issued a Draft Law to amend the Enforcement Decree to the International Tax Adjustment Act. This provides for detailed provisions for the application of the QDMTT and will also extend the Transitional CbCR Safe Harbour by 1 year (as provided in the January 2026 OECD Side-by-Side Package).

On January 19, 2026, the Hong Kong Inland Revenue Department opened its E-filing portal for the submission of Top-Up Tax Notifications
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |